MyPass Connector for MSSQL
The MyPass Connector for Microsoft SQL Server enables automated discovery, management, and rotation of native SQL Server logins across multiple instances from a single MyPass deployment. Installed automatically with the MyPass Gateway Server and licensed separately on a per-managed-account, per-system basis, the connector executes all operations from the Gateway using standard TCP/IP communication (default port 1433) with optional TLS encryption. Password changes are performed securely by calling a pre-deployed stored procedure in the target database that contains the actual reset logic (ALTER LOGIN), eliminating the need for agents on the SQL Server hosts. Configuration is centralized in the MyPass Administration Client, requiring only network connectivity, a dedicated service account with minimal privileges, and the one-time deployment of the vendor-supplied stored procedure — delivering a secure, auditable, and low-maintenance integration for native SQL Server accounts.
Quick Implementation Pointers (UPDATE)
- Verify Network and Infrastructure Pre-requisites
- Configure the target Microsoft SQL Server Instance
- Optional: Enable Encrypted Connections (TLS)
Network and Infrastructure Pre-requisites
To ensure successful integration, the following network and infrastructure components must be in place:
- MSSQL Environment: A functional Microsoft SQL Server instance with TCP/IP enabled and accessible, configured to support standard SQL authentication.
- MyPass Gateway Server: A Windows Server (2016 or later) to host the MyPass Gateway application, acting as a secure intermediary between the MyPass Password Manager Servernector.
- Network Connectivity: Open firewall ports for TCP 1433 between the Gateway Server and MSSQL instance/s.
- Stored Procedure: The password reset logic must be implemented as a stored procedure within the target MSSQL database. This procedure must be deployed before integration.
- System Account: A SQL Server account with sufficient privileges to execute password reset operations, including
ALTER LOGINcommands. - Encryption Configuration (Optional): If encryption is enabled, the MSSQL server must be configured to support encrypted connections.
Required Configuration Parameters
To access an MSSQL server, the following parameters must be configured in the Administration Client:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Hostname | Fully qualified hostname, simple hostname, or IP address. |
| Port | Port MSSQL is listening on (e.g., 1433). |
| Instance | The MSSQL instance to connect to. |
| Database | The database containing the stored procedure. |
| Stored Procedure | Name of the stored procedure to execute. |
| Account | Account with privileges to execute ALTER LOGIN commands. |
| Password | Password for the specified account. |
| Encryption | Boolean flag to enable encryption (requires additional server config). |
These parameters are used to construct a valid MSSQL connection string. The Administration Client allows customization beyond these defaults. Sensitive data such as account credentials and connection strings are stored in ADAM with strong encryption.
Configuring MSSQL for MyPass Connector
The connector uses standard MSSQL connection strings and supports all MSSQL communication methods. However, MyPass has only been tested with TCP communication.
Steps to configure MSSQL for MyPass Connector
MSSQL Communication Settings
To configure TCP communication in MSSQL Server 2005 Express on Windows Server 2003:
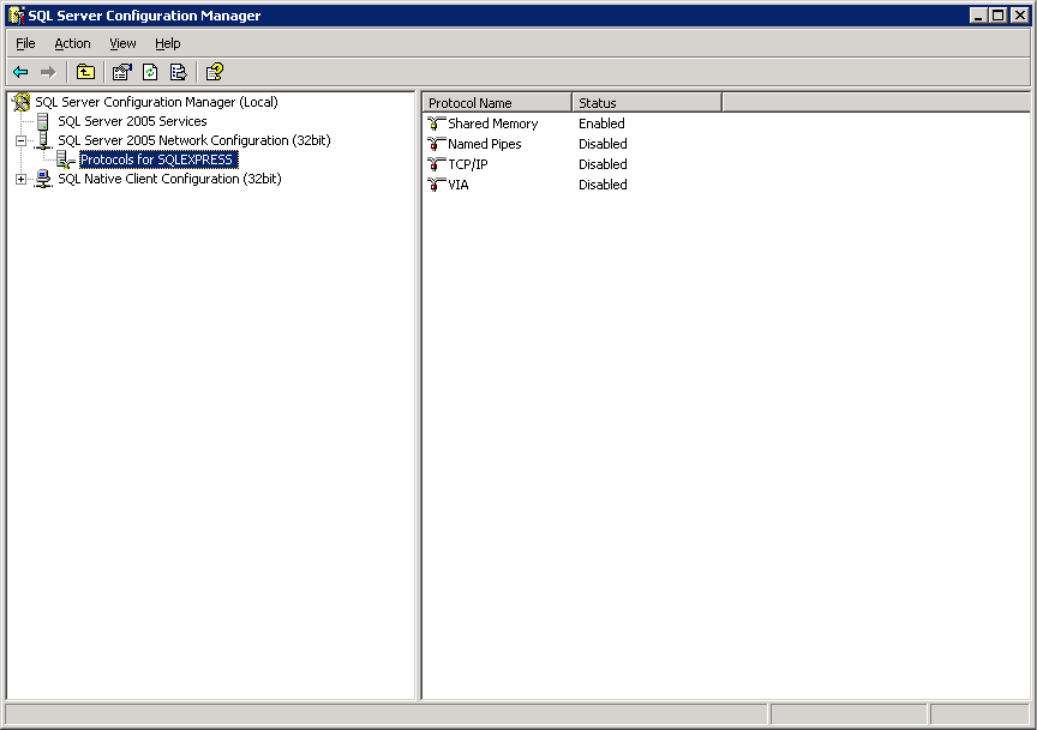
- Open SQL Server Configuration Manager via
Start → Microsoft SQL Server 2005 → Configuration Tools → SQL Server Configuration Manager.
- Navigate to Protocols for [Instance], right-click TCP/IP, and select Properties.
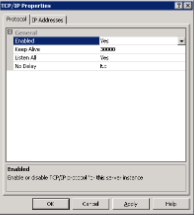
- In the Protocol tab, set Enabled to
Yes.
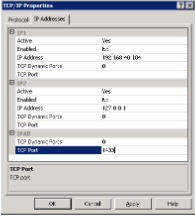
- In the IP Addresses tab, under IP All, set the desired TCP Port (e.g.,
1433).
- Click OK and restart the MSSQL service.
MSSQL System Account Configuration
To configure the MSSQL system account:
Open Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio and log in as
SAor another admin account.Navigate to
Security → Logins.Right-click Logins and select New Login.
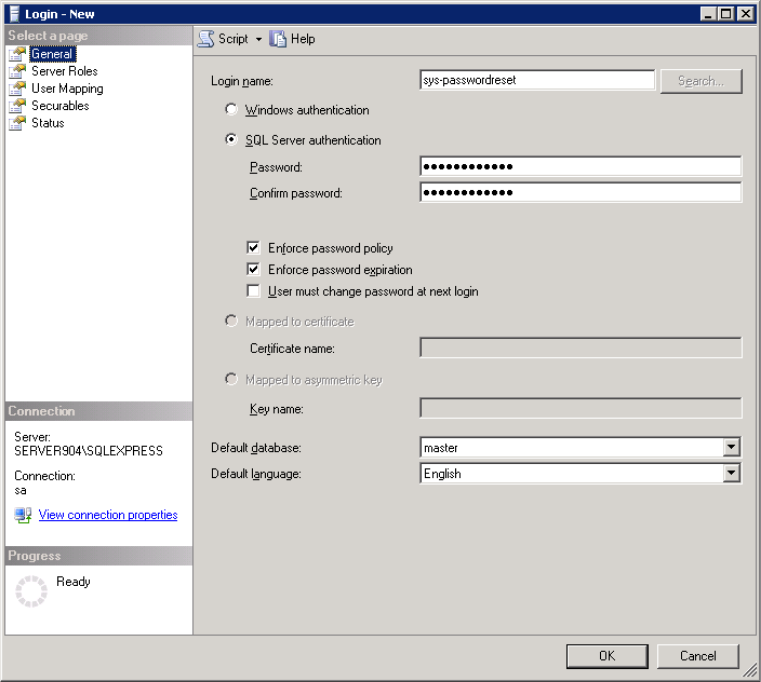
On the General page:
- Specify the Login name.
- Select SQL Server authentication and set a password.
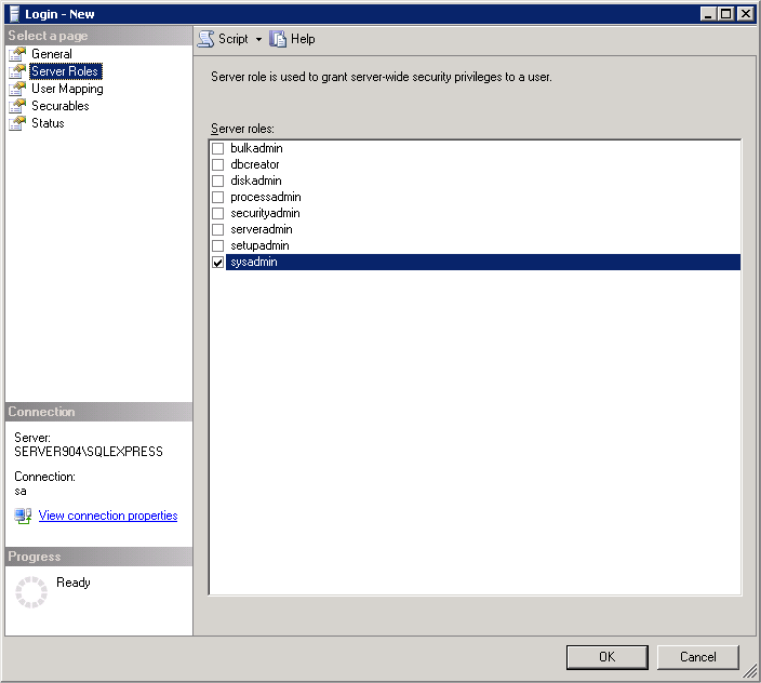
- On the Server Roles page, assign the sysadmin role.
- Click OK to create the account.
MSSQL Stored Procedure Configuration
To configure the stored procedure:
- Open SQL Server Management Studio and log in as
SAor the newly created account.
- Navigate to
master → Stored Procedures.
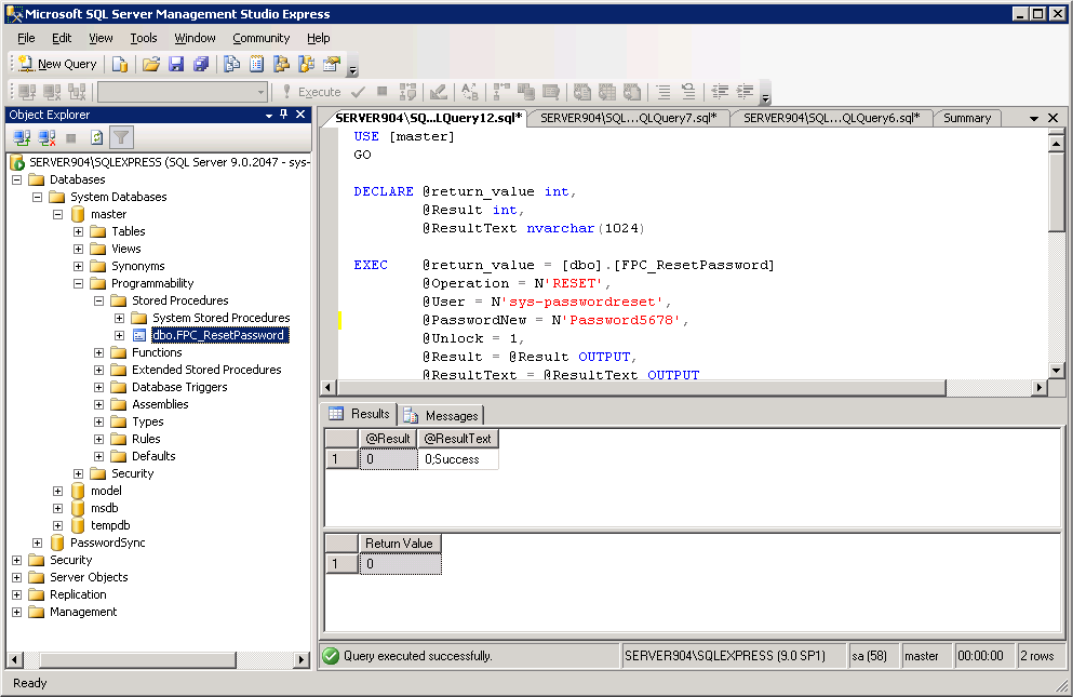
- Right-click Stored Procedures and select New Stored Procedure.
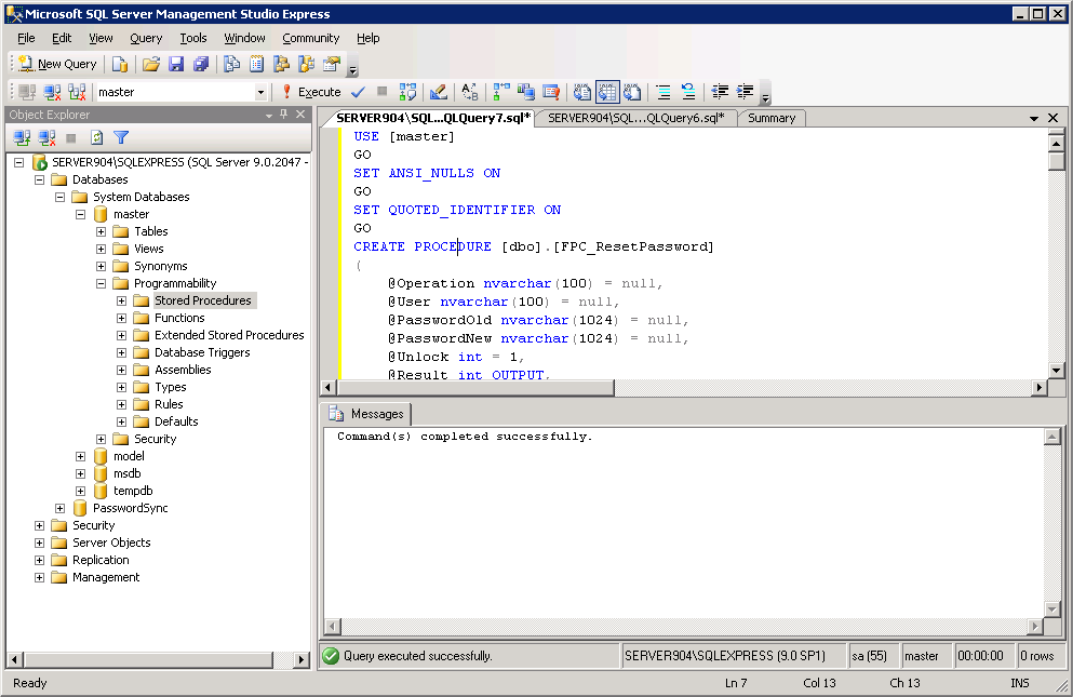
- Paste the contents of
<installdir>\MyPassCorp\MyPassGateway\bin\ConnectorMSSQL\FPC_PasswordReset_ForDatabaseUsers.sql.
- Click ! Execute on the toolbar.
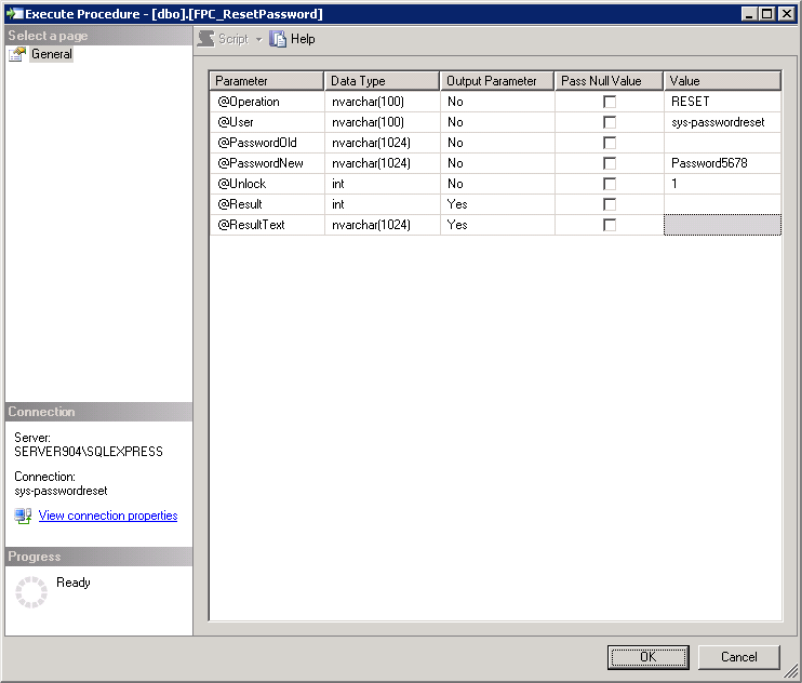
- Expand Stored Procedures, right-click FPC_ResetPassword, and select Execute.
- Fill in the required parameters and click OK.
If successful, the result will confirm that the MSSQL environment is ready for integration with the MyPass Password Manager solution.
Enabling Encrypted Connections (TLS)
- Install a valid certificate on the SQL Server (or use self-signed for testing).
- In SQL Server Configuration Manager → Protocols → Force Encryption = Yes (optional).
- Set Encryption = true in the connector configuration.
- Ensure the Gateway Server trusts the SQL Server certificate.
Licensing – Simple Summary
| What you pay for | How it’s calculated |
|---|---|
| Active Directory (required) | One fee per managed user |
| Each additional system (Microsoft SQL Server) | Additional fee per managed user × per SQL Server instance |
Real-world example
If you manage 1 000 users:
- Active Directory → 1 000 × base user license
-
- 5 SQL Server instances (e.g., Prod, Dev, Reporting × 2, DR) → + 5 000 × MSSQL connector user license (1 000 users × 5 instances)
- Total = base AD license + MSSQL connector license for 5 000 “user-instance” seats
Simple and fair - you only pay for the SQL Server native accounts that MyPass actually rotates.